Agreement
We use cookies on our website to provide you with the best possible experience. By clicking "Accept All" you agree to the use of all cookies and to our privacy policy.
The digital signature (or e-signature, eSignature, etc.) has become an indispensable tool for companies and individuals to manage documents in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way. In this article, we provide a starting point for anyone who wants to bring an old process - signing documents - up to date.
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a secure and efficient method of signing contracts in a digital environment as an alternative to handwritten signatures.
The digital signature works like a human fingerprint, as each document has its own unique electronic fingerprint. No other document can have the same digital signature. If a digital document is "sealed" with a signature, it can be proven that
- the file has not been changed after signing (integrity).
- a specific person has signed the document (authentication).
- the signatory actually signed the document. The person cannot deny having signed the document after a digital signature has been created.
- the document is not a forgery.
Digital signatures are already used in many industries for a wide variety of applications.
What is not a (valid) digital signature?
Only a signature that can also be verified by an approved online verification service (e.g. Acrobat Reader, RTR, or directly in sproof sign) can be classified as legally compliant.
A scanned image of a handwritten signature does not create a legally signed document and is not legally valid!
The eIDAS Regulation regulates for Europe how documents can be signed in a legally valid and verifiable manner. You can find out more here.
How digital signing of PDF documents works
Applying a valid digital signature to a (PDF) document is a technically complex process that runs unobtrusively in the background when digitally signing a document.
A correct digital signature therefore differs significantly from simply inserting a scanned handwritten signature.
A valid digital signature allows subsequent changes to the document to be recognized. This is not the case when simply inserting images.
This is how digital proof of intent works with a signature platform:
Step 1: Upload and conversion
First, you upload your document online via your account on a signature platform. The document is converted into a PDF document.
Step 2: Applying the digital signature
For the signature itself, you need a digital certificate that proves your identity as the signatory. This is created for you when you register on a signature platform. If you want to sign with the highest standard, the qualified electronic signature , this step is carried out by a state-recognized certification authority .
With a signature platform, you have the option of customizing your signature (similar to the handwritten version) and creating your own signature style.
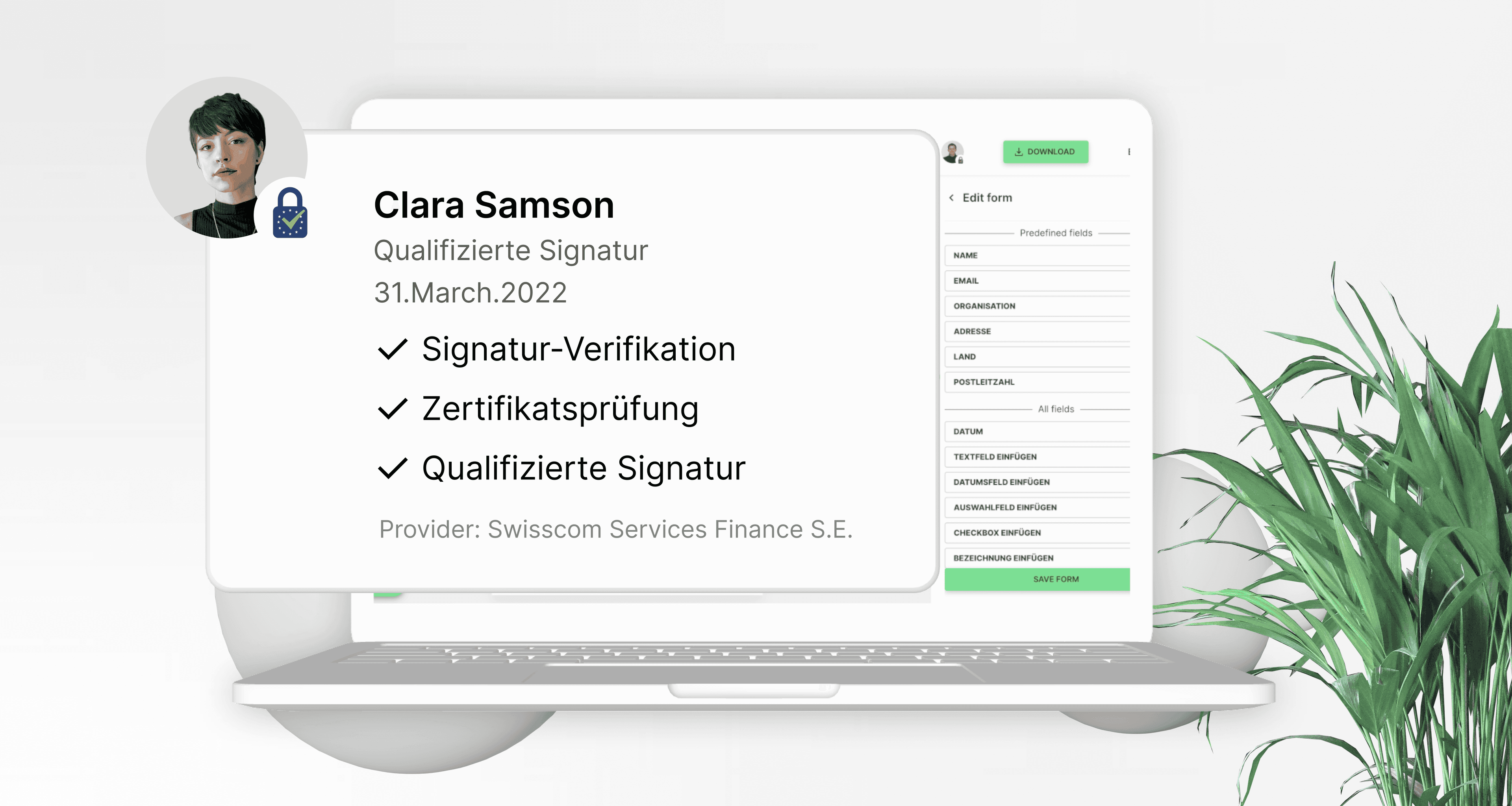
Step 3: Encryption of the document and the signatures
In the final step, the entire contract, including the attached signatures, is cryptographically encrypted. A so-called hash value is generated. The contract becomes forgery-proof and verifiable.
The attached signatures have the highest probative value and can no longer be forged.
Of course, the signed contracts can be downloaded, sent or saved anywhere.
Can I also sign digitally in Word or other Office programs?
In principle, many file formats can also be digitally signed. However, in order for the applied digital signature to be unalterable, each document must first be converted into a PDF document. As is well known, PDF documents can no longer be changed (unlike docx documents, for example). Digital signature platforms automatically convert many file formats into a correct PDF document, usually when the document is uploaded.
How do I get a digital signature?
There are various ways to obtain a digital signature.
Registering with a digital signature platform (AES)
As already explained, the creation of a digital signature is the central element of a digital signature platform. Established and well-known solutions are, for example, DocuSign , AdobeSign or newer European solutions such as sproof sign or yousign, which have also specialized specifically for use in European companies.
An advanced electronic signature is created for you when you register.
Identification with a signature platform (QES)
Many providers also equip users with a qualified electronic signature, which is deeply integrated into the application itself. In addition to the high evidentiary value of this signature standard, you benefit from the many options for customizing your signature process.
Identification with a government service (QES; e.g. cell phone signature)
In Austria, more than 50% of citizens already have a cell phone signature. This is issued by public authorities and complies with the qualified electronic signature standard.
Legal validity of a digital signature
A valid contract is concluded when both parties express their consent. The legislator generally leaves it up to the contracting parties to decide whether they conclude a contract verbally, in writing or electronically. This is known as freedom of form.
If you opt for a digital signature solution, you have the advantage that all signatures are integrated into the PDF file in an unalterable and forgery-proof manner.
There are only very few exceptions where electronic signatures are still excluded by law, despite constant amendments to the law. One example: a will.
Either way, it is necessary to select the right e-signature standard depending on the contract.
Three standards have been established for this, which are defined in the eIDAS Regulation and serve as a legal framework.
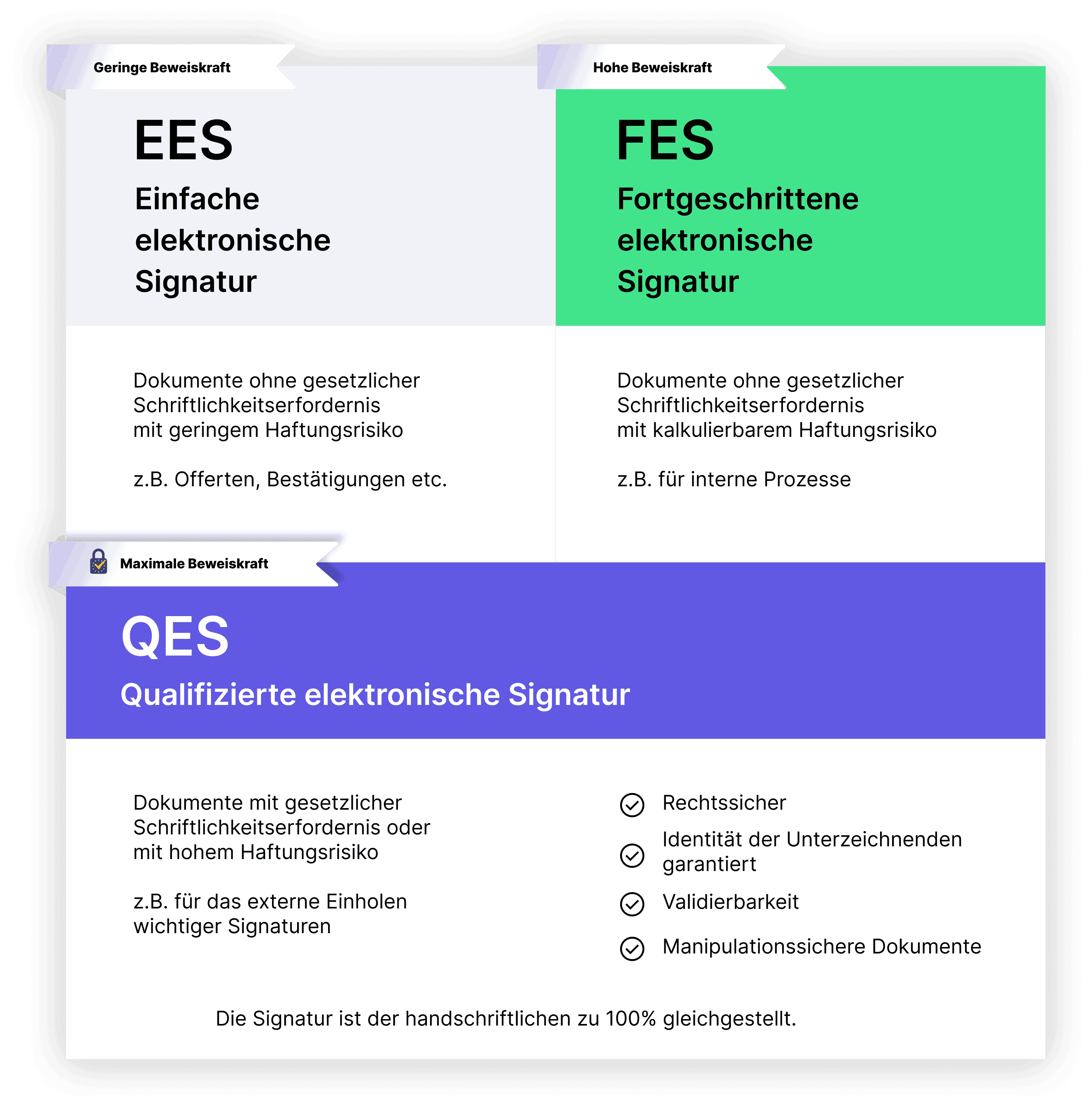
- Simple electronic signature (EES)
- Advanced electronic signature (AES)
- Qualified electronic signature (QES)
The qualified electronic signature (QES) meets the highest quality criteria and is legally 100% equivalent to a handwritten signature.
As the legal implications can vary widely, factors such as implementation costs, ease of use (customer experience), legislation, company policies and the assessed business risk will usually determine which method should be used in a particular situation.
You can use the following decision guide to help you.
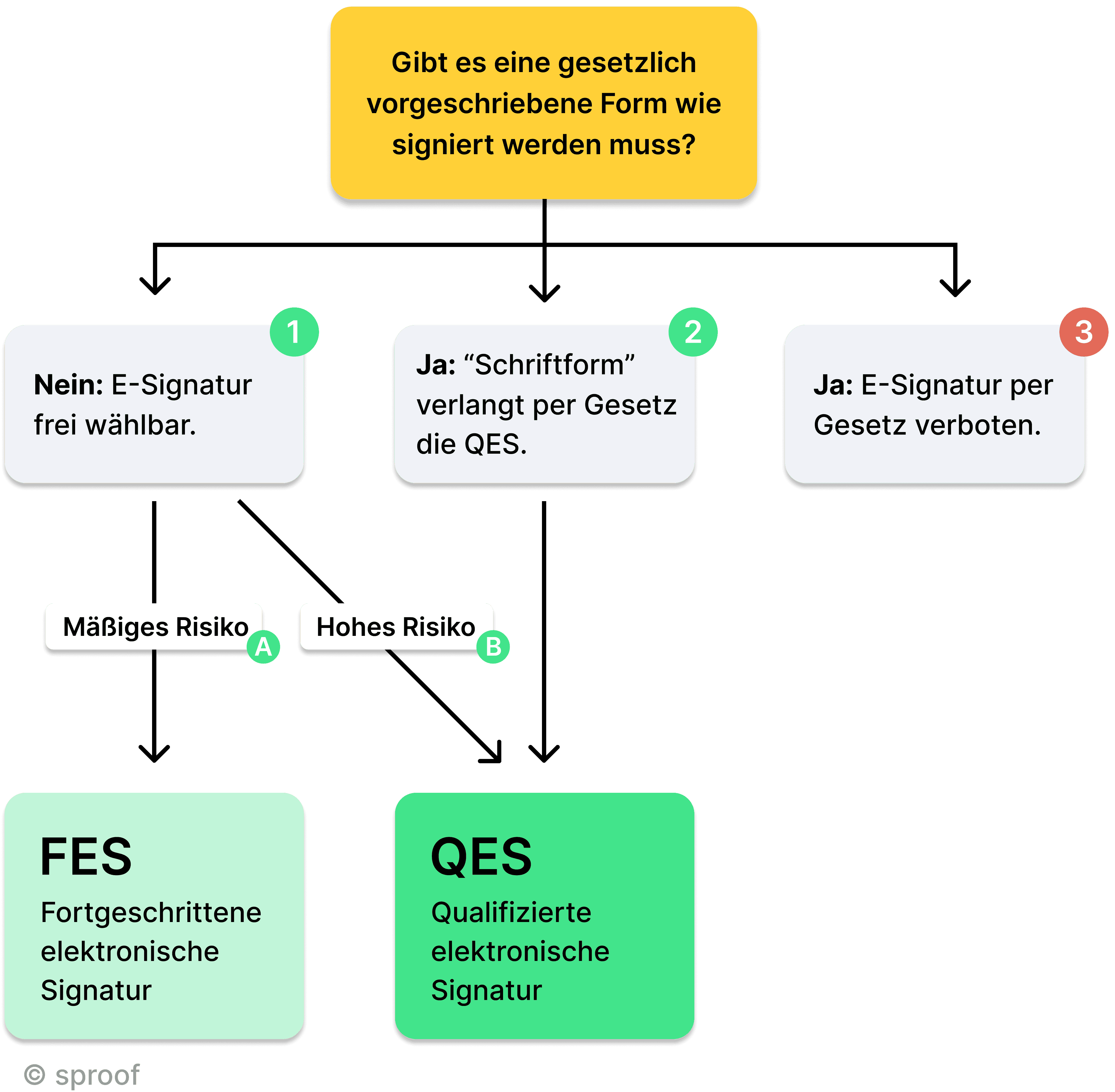
Two factors therefore influence the choice of the right standard for the electronic signature:
- Liability risks, operational risks
- Legal requirements
The advantages of a digital signature platform are that you can
- you can change the e-signature standard at any time depending on the type of contract
- you can specify the desired e-signature standard when procuring external signatures.
European signature providers have mostly focused on the two highest digital signature standards.
sproof sign is an expert in the field of qualified electronic signatures (QES) in particular.
Is a scanned signature or signature image valid?
The term "scanned signature" means that it is a digital image of a handwritten signature. The original paper signature is converted into a digital format (.jpg, .doc, .pdf etc.) using a scanner or camera.
In principle, such scanned signatures are valid as long as no written form is required for the corresponding declaration of intent.
A signed copy is not legally valid as the signatory cannot be identified and consent cannot be proven.
A scanned signature is easy to forge so that the recipient of the signed contract can easily copy it (#SnippingTool #Screenshot). It is obvious that this is not legal.
A scanned signature has no probative value in court, as it is only a copy of your original signature. Without proof of how the signature was made, it is considered a mere copy and not an authentic signature. For this reason, it is invalid, especially in business transactions.
The difference between a digital signature and an electronic signature?
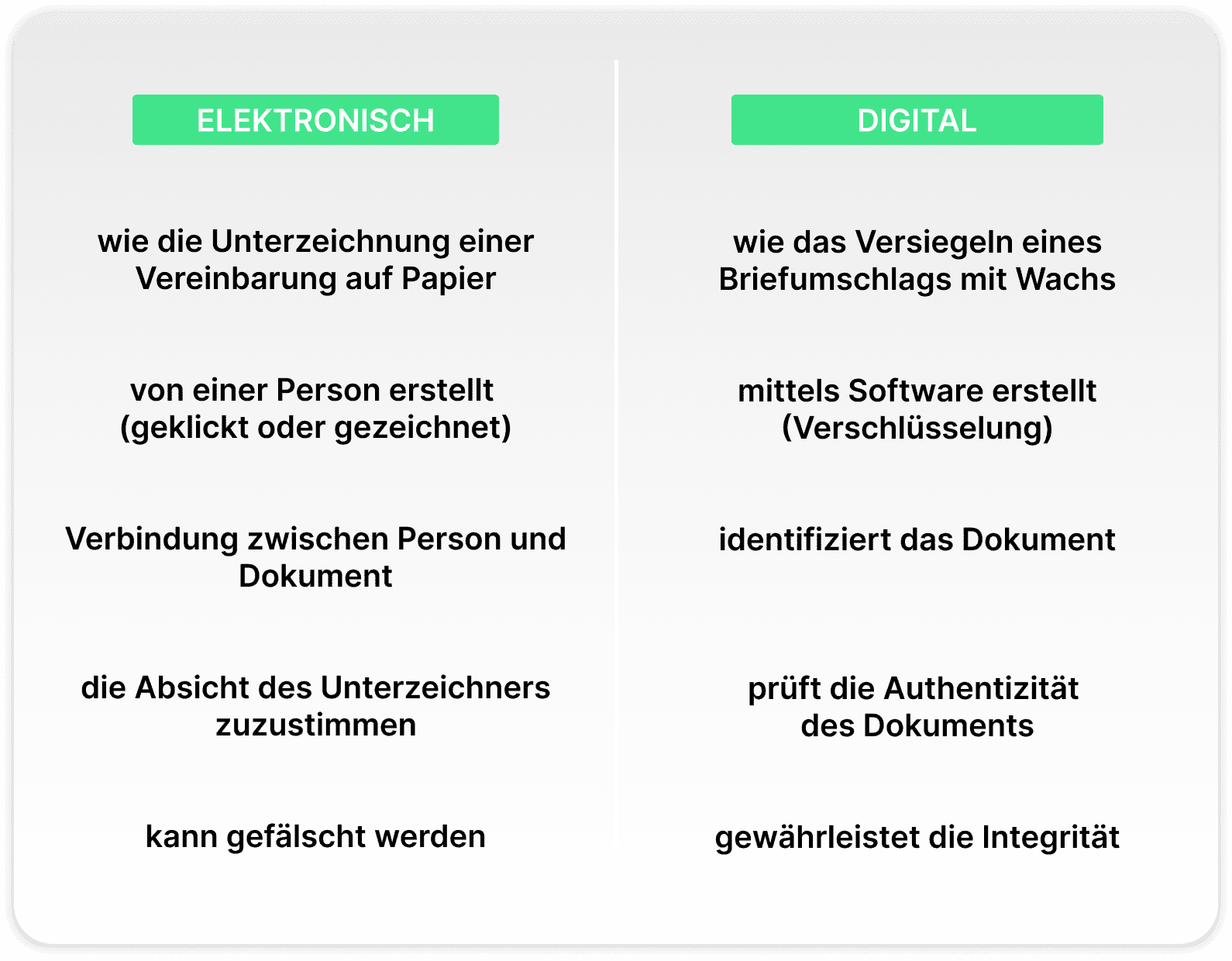
The terms "electronic signature" and "digital signature" can easily be confused. The terms are often used interchangeably, but strictly speaking they are not the same thing.
An electronic signature (or e-signature) is a method of concluding a legal agreement in a digital environment. It is, so to speak, the digital equivalent of signing a paper document.
While the electronic signature proves the consent of the signatory of the document, the digital signature is proof of the authenticity of the document itself. This means that the combination of document and signature has been technically designed and encrypted in such a way that the contract is forgery-proof. The terms thus merge or work together in such a way that a digital agreement becomes verifiable and legally enforceable.
The advantages of a digital (European) signature platform
Highly secure cloud, readyto go sproof sign is a web-based solution for digitally signing contracts and works on all mobile devices (desktop, smartphone, tablet). sproof sign is based in Austria and all data is backed up exclusively in data centers within the EU. We guarantee GDPR compliance at all levels, both with us and with our subcontractors. We offer our customers these guarantees in an order data processing contract (ADV), which is based on the EU standard contractual clauses and therefore also offers maximum legal certainty.
Interfaces & existing systems
- sproof sign can be seamlessly integrated into your existing systems.
- Sign directly in common tools such as MS Teams, Word, Google Drive etc. (list of all integrations ).
- Single Sign On
- Simple API for customized use cases. (API documentation )
Document storage & progress controlImportant contracts are stored in a central location in a clear, highly secure and encrypted manner. Nevertheless, documents can be accessed at any time and from any location. In addition, the progress of the signature processes can be viewed at any time and reminders can be sent if required.
Qualified (QES) and advanced (AES) electronic signing including identification. sproof sign supports all types of electronic signatures (simple, advanced and qualified) in accordance with the eIDAS Regulation as well as many other globally used signature standards (e.g. FDA compliance). You can sign within your organization as well as with external partners, suppliers or customers.
Batchsignature: sign contracts at the same timeWith the batch signature, countless documents can be digitally & legally signed in a single operation. An enormous time saving.
Document folder: send contracts at the same timeStaple several documents together digitally and send them together for signature. This saves you and the recipient a lot of time.
Company branding, company stamps & signature stylesWhether you are a large team or an individual user. In sproof sign, you can store your own company logo as a company stamp. You can also create different signature styles for different purposes.
eID Hub: Obtain signatures throughout EuropeThe qualified signature is legally equivalent to the handwritten signature throughout Europe. sproof sign enables the signing of contracts with various qualified signature providers with its unique interface. This is a huge advantage when obtaining and issuing legally valid signatures. Click here for an overview of all integrated trust service providers →
Verify signatures & download verification reportsYou can check the validity of the electronic signatures applied directly in sproof sign with a click of the mouse. You can also download a verification report for each signature run and see who signed with which certificate and when.
Team management & substitution rulessproof sign enables simple user and rights management for users within a plan. In addition, the signature quota can be managed centrally and various important settings can be made for the entire plan.
Support & Academysproof sign is known for its fast and flexible support. The sproof sign Academy is a free training portal that helps you and your employees get off to a quick start.
Transparent pricing with no hidden costsOur aim is to be the unrivaled best bidder in the search for a suitable signature provider. In doing so, we place great value on fairness and transparency. Two values that characterize our corporate culture. These values also determine the pricing of our solution in the enterprise segment.
More blog entries
How KURZZEiTmiete optimizes its customer journey with sproof signTeam Axess chooses digital signature solution from sproof signWhat is the eIDAS Regulation? Basics & advantages at a glanceNIS-2 directive and digital signatures: a step towards greater security in the digital worldW&H Dentalwerk: Successful integration of sproof sign for medical technology